Commonly known as breast pain among the public, mastalgia is a condition that almost every woman experiences once or several times in her life. It is seen less frequently in young girls who have a regular menstrual period. However, sometimes the intensity and frequency of pain may increase during menopause. Although the causes of mastalgia are not certain, breast cancer may occasionally cause this type of pain. Most of the time, however, these pains occur due to muscle and joint pain.
The treatment of mastalgia is often based on the cause of the pain. Therefore, accurately identifying the factors causing the pain is extremely important for the treatment process. Very severe mastalgia is observed under clinical conditions by specialists.
Istanbul has many specialist doctors who can diagnose severe breast pain that requires mastalgia treatment. Many clinics provide services in this field, in particular. Mastalgia treatment prices are determined according to how the treatment will proceed and may vary depending on what the treatment includes.
Determining the correct treatment for mastalgia is important for the health of patients. The progress and application of the treatment is valuable not only for patients but also for the relatives of the patients. During this process, patient relatives will want to have sufficient information about mastalgia. In this article, we will provide detailed information on the symptoms, stages, and risks of mastalgia; mastalgia treatment options; the types of mastalgia treatment, treatment risks, and the post-treatment process.
| Types of Pain | – Cyclical Mastalgia: Pain associated with menstruation. It typically appears before the menstrual period and is felt in both breasts. – Non-cyclical Mastalgia: Occurs outside of the menstrual cycle, can be constant or intermittent, and is usually felt in only one breast. |
| Causes | Hormonal imbalances (especially estrogen and progesterone), the presence of cysts or fibroadenomas, certain medications (oral contraceptives, hormone therapies), trauma, or stress. |
| Symptoms | Sensitivity, a burning sensation, continuous or intermittent pain. Cyclical pain generally aligns with the menstrual cycle, while non-cyclical pain appears at irregular times. |
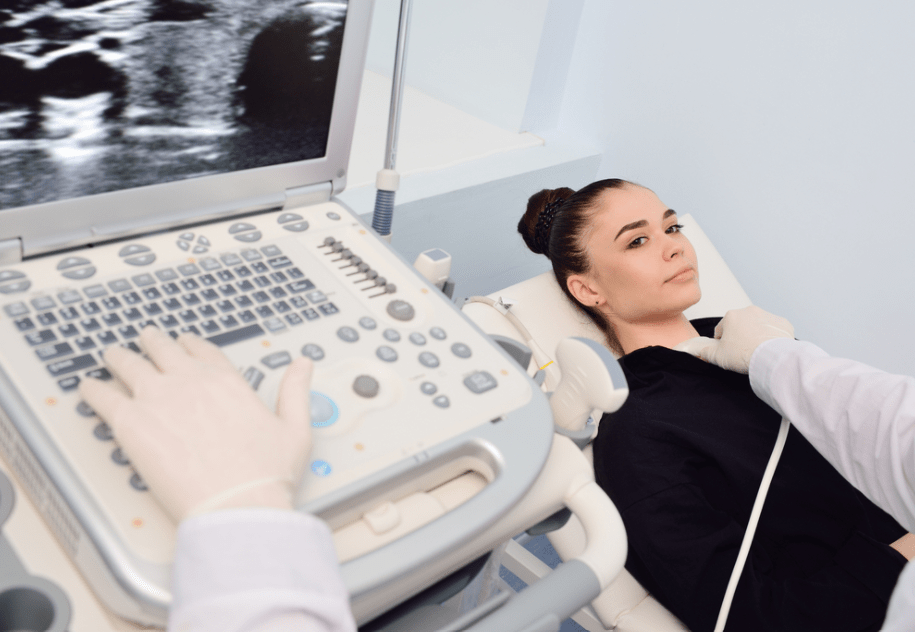
| Diagnostic Methods | – A physical examination is performed, and the region and type of pain are evaluated. – If necessary, a mammogram or ultrasound is taken. – If the cause of non-cyclical pain is unknown, a biopsy may be performed. |
| Treatment Methods | – In cyclical mastalgia, hormone-regulating medications (birth control pills) or estrogen-suppressing drugs may be used. – For non-cyclical pain, pain relievers (NSAIDs), dietary and lifestyle changes. – Physical therapy or relaxation techniques may also help. |
| Complications | If the pain becomes chronic, there may be a decrease in quality of life. Other than that, serious complications are rare. |
| Lifestyle Recommendations | Using a supportive bra, reducing caffeine and salt intake, reducing stress, and engaging in regular exercise are recommended. |
| Follow-up | Regular medical check-ups are recommended in cases of persistent or severe pain. |
What Is Breast Pain?
Breast pain, medically referred to as “mastalgia,” is a commonly encountered problem among women. Breast pain can occur for many different reasons and is a natural part of a woman’s menstrual cycle.
However, breast pain can also be an indicator of different illnesses depending on the severity and frequency of its occurrence. Pain associated with the menstrual cycle constitutes a large portion of breast pain. Therefore, if you have breast pain outside of the natural and usual pain experienced during the menstrual cycle, you should definitely consult a healthcare facility.
Breast pain can occur at any age but most frequently affects women in their premenopausal (30-50 years old) period. Its exact cause is not known. However, hormonal, dietary, and psychological factors can be effective in the development of mastalgia.
The pain is usually moderate and tolerable, but in 10-20% of patients, it can be severe enough to negatively affect daily life and require treatment.
Breast pain is not very common in breast cancer, but all patients with mastalgia should undergo a breast examination and appropriate breast imaging techniques. Treatment should be initiated according to the identified cause, and the patient should be placed under clinical follow-up.
What Are the Causes and Treatment of Breast Pain?
It can occur at any age but most frequently affects women in their premenopausal (30-50 years old) period. Its exact cause is unknown. However, hormonal, dietary, and psychological factors can be effective in the development of mastalgia.
The pain is usually moderate and tolerable, but in 10-20% of patients, it can be severe enough to negatively affect daily life and require treatment. Breast pain is not very common in breast cancer, but all patients with mastalgia should undergo a breast examination and appropriate breast imaging techniques. Treatment should be initiated based on the identified cause, and the patient should be placed under clinical follow-up.
Are There Types of Breast Pain?
Yes, there are various types of breast pain. The most typical type is cyclical breast pain, which is related to the menstrual cycle and hormonal changes. This type of pain, typically felt in the upper, outer part of the breasts, usually affects both breasts. It can be sharp or dull, and there may be swelling or fullness accompanying it.
Non-cyclical breast pain, which is not related to the menstrual cycle, is another type of breast pain. This type of pain can be caused by injuries, infections, or certain conditions such as breast cancer or fibrocystic breast changes. Non-cyclical breast pain can occur in one or both breasts and may be constant or sporadic. It can present as lumpy, red, warm, or dull, and can also be sharp or dull.
How Does Breast Pain Go Away?
Mastalgia, also known as breast pain, can receive various treatments depending on the source of the pain. Non-cyclical breast pain, or pain not related to the menstrual cycle, can often be treated with lifestyle changes such as wearing a bra that supports and warms the affected area.
Wearing a supportive bra and engaging in stress-reducing activities can help treat cyclical breast pain, which is associated with the menstrual cycle. If the pain is severe or persistent, a healthcare professional should be consulted for further testing. A breast care specialist may suggest additional treatments like physical therapy or nerve blocks. It is very important to remember that self-treatment for breast pain should never be undertaken without first consulting a healthcare professional.
What Are the Symptoms of Breast Pain?
Breast pain can arise for many different reasons. Symptoms that may accompany breast pain include:
- Pain that may be located in a specific area of the breast or throughout it, in one breast or both, related to the menstrual cycle or independent of it, and ranging from mild to severe.
- Rash, dryness, or cracking may occur on the breast skin or nipple.
- Redness, increased warmth, and edema may appear in the breast.
- Clear, purulent, or bloody discharge may be seen from the nipple.
- A lump may be felt in the breast tissue.
How Is Breast Pain (Mastalgia) Treated?
In treating breast pain, it is crucial to correctly identify the underlying cause first. A detailed medical history obtained by a specialist is essential for diagnosis, and a comprehensive physical examination can lead to a diagnosis.
If necessary, the doctor may use additional diagnostic methods such as mammography and ultrasonography. A suitable treatment method is determined based on the identified disease and its causes. The most common cause of breast pain is hormonal changes.
Therefore, the approach to treatment is often in the form of lifestyle changes.
Possible treatment methods that may be recommended by a doctor include:
- It may be necessary to take a break from hormone therapy or other medication treatments for a period.
- Bras that support the breast and are compatible with its size should be worn.
- Breast pain can increase with caffeine consumption. Therefore, the consumption of beverages like coffee and tea may be limited.
- A healthy diet should be adopted.
Frequently Asked Questions About Mastalgia (Breast Pain)
What does mastalgia mean?
Mastalgia, which 70% of women experience at some point in their lives, is the name given to the swelling, tenderness, pain, and feeling of heaviness that occur in the breast, around the breast, or in the armpit area. Most of these pains are hormonal in origin.
What causes mastalgia?
Seen in 1 out of every 2 women, mastalgia can be caused by hormonal changes (pregnancy, menstruation, menopause, etc.), fibrocystic changes, certain medications, and sometimes chest pain can be seen rarely after heavy or unfamiliar physical activities due to trauma.
How can mastalgia go away?
In order to relieve breast pain, the underlying cause must first be identified. In addition to a physical exam, other imaging methods such as mammography and ultrasonography, and laboratory techniques may be used for an accurate diagnosis. A treatment protocol is prepared based on the results. Since it is usually due to hormonal factors, changes in lifestyle can effectively help reduce breast pain. (Choosing the right underwear, reducing caffeine consumption, opting for low-fat foods, etc.)
What causes a stinging pain in the breast?
Patients can describe pain in their breasts in various ways. One such description is a stinging pain, which usually originates from the musculoskeletal system and is perceived as breast pain due to the adjacency of that region.
Why does a woman’s breast hurt?
There can be many reasons for breast pain in a woman. The most common cause is related to one of the most frequent symptoms of premenstrual syndrome: breast pain. Also, breast pain can occur due to pregnancy, breastfeeding, blocked milk ducts, cysts, abscesses, or, rarely, breast cancer.
Which doctor should I consult for breast pain?
Women experiencing breast pain, which is quite common, should consult a specialist general surgeon.
Does breast pain spread to the arm?
Breast pain can sometimes manifest as burning, stinging, or throbbing. This type of pain can usually spread to the arm and armpit.
Is every breast pain a sign of cancer?
Breast pain is quite common, and there are women who experience this complaint every month. The most important reason for breast pain is structural, so its connection to cancer is minimal. If a person experiences constant breast pain, they should consult a doctor.
Which medications cause breast pain?
Some medications may cause breast pain. In particular, antidepressants, cholesterol-lowering medications taken with hormones, and heart medications can lead to breast pain.
Is it normal for breast pain to continue after menstruation ends?
It is possible to experience breast pain around 7 to 3 days before menstruation. However, some women continue to experience breast pain after menstruation ends. This may be due to periodic or non-periodic breast pain. In the case of periodic pain, rising estrogen levels stimulate the breast tissue, causing pain and tenderness. Non-periodic breast pain, on the other hand, has no relation to the menstrual cycle. It can be intermittent or continuous.
References:
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15469-breast-pain-mastalgia







İstanbul'daki Muayenehane Konumu